Clínica Boj » Dental esthetics » Dental dislocation or displacement
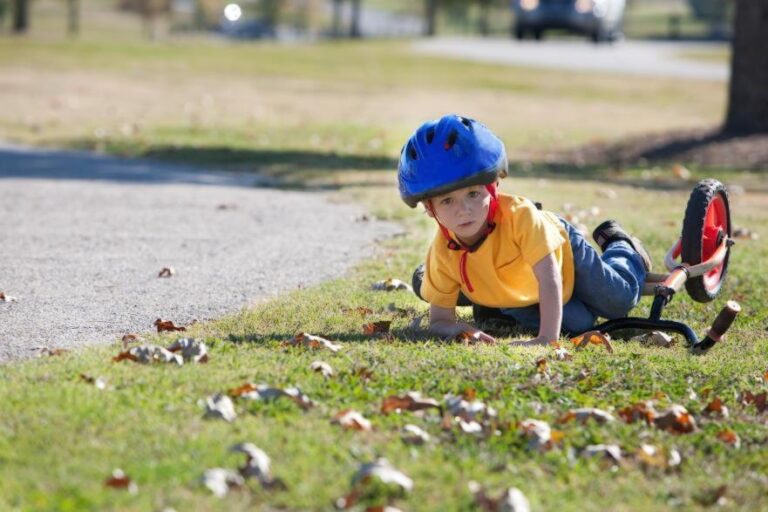

Dental trauma is a very common injury in childhood and adolescence that occur in teeth and jaws as a result of an accidental physical impact. Among the types of orofacial traumas, tooth luxation or subluxation are very common. These can endanger the vitality and prognosis of the tooth.
A tooth displacement, known as “dental luxation” within the field of dentistry, is a movement of the tooth with respect to its normal position. This displacement can occur in the vertical or anteroposterior plane. Depending on the case, we specialists in paediatric dentistry call it luxation or dental subluxation.
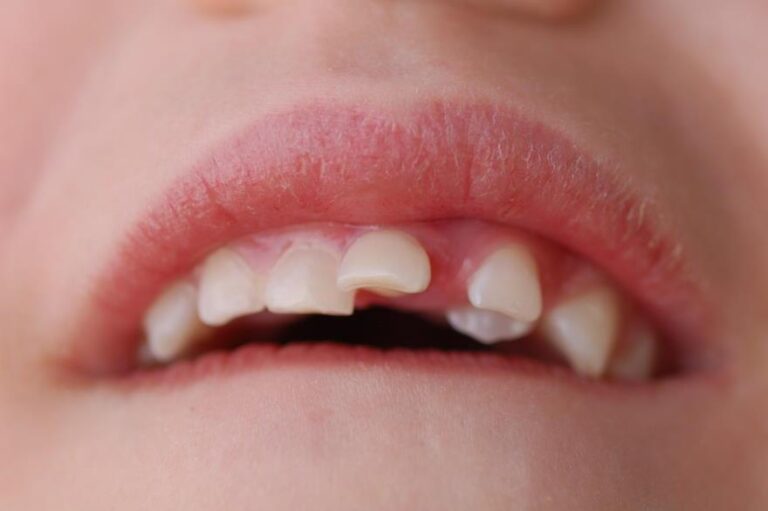
The mobility is usually due to inflammation of the periodontal ligament or because the periodontal fibers (which connect the root of the tooth to the alveolar bone or structures where the tooth is supported) have been sectioned in a dental luxation or subluxation. Sometimes we also find mobility due to a root fracture of the tooth. The most advisable attitude to adopt is to resort to a dentist specialized in children, where he will be able to make a correct diagnosis and propose to parents and children the appropriate approach to preserve tooth vitality.
Intrusive dental luxation means there was a displacement of the tooth to the lowermost parts of its support structures, this would mean there is a collapse of the tooth into the alveolar bone or structures that support it. This means that the tooth can be seen or perceived apparently smaller than observed before the dental trauma. Given the case, it is essential that the paediatric dentist correctly diagnose each case by means of radiographs and plans a treatment to maintain the vitality of the tooth.
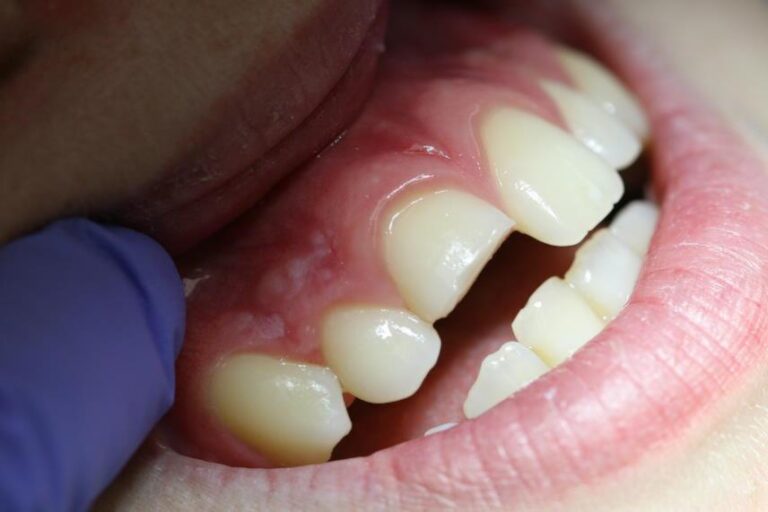
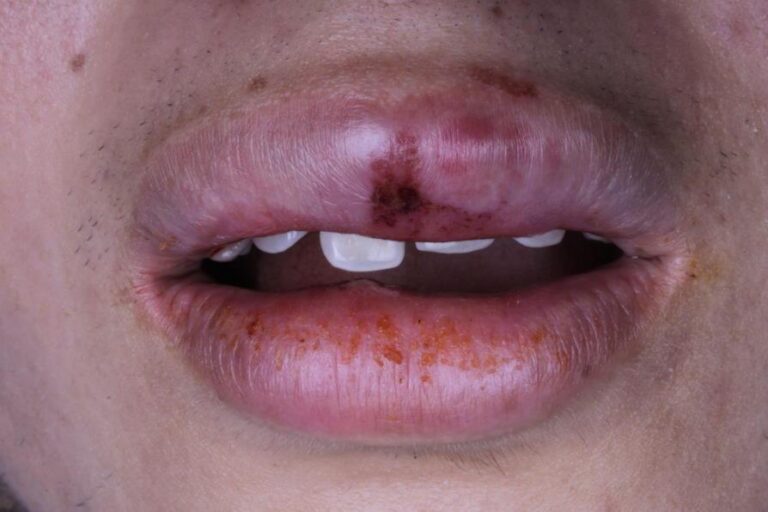
Dental extrusion or extrusive dental luxation after a trauma is characterized by the collapse of the fibers of the periodontal ligament holding the tooth, which clinically is observed as a tooth outside its supporting structures meaning the place where the tooth is held. This would cause the tooth to be perceived larger than it was in its normal position prior to the accident. As in other traumas, immediate attention by a paediatric dentist is essential so that the prognosis of maintaining the vitality of the tooth is the best possible.
Dental concussion is the most benign of dental trauma forms, so it is very unlikely that the tooth loses its vitality. In a dental concussion there is a lesion of the supporting structures of the tooth, although it is not mobile and it is in its normal position within the dental arch.

We use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. We do this to improve browsing experience and to show (non-) personalized ads. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.