Clínica Boj » Dentistry for babies

Dentistry for babies
The paediatric or child dentist is trained and prepared to appropriately take care of the child from the earliest stages of life, which is why he or she can also be entitled as a baby dentist.
Baby Dentistry
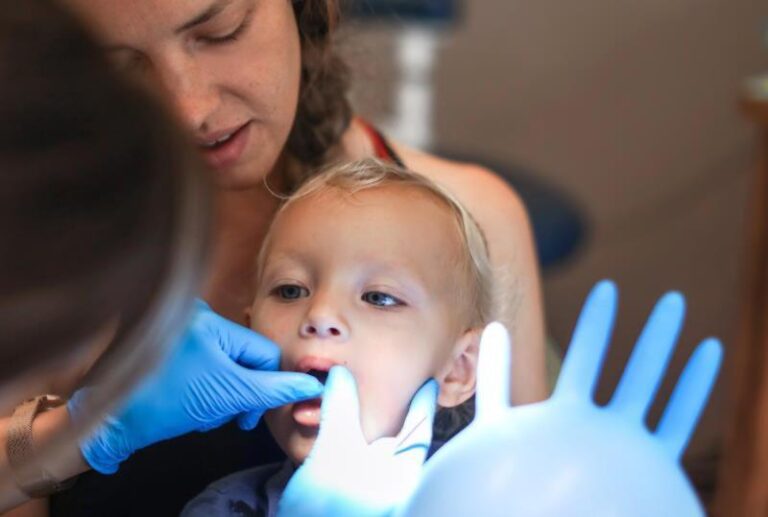
Paediatric dentistry specializes in the care of babies, commonly known as “Odontobebé” in Spanish or “Dentistry for babies”, or both, and is essential to prevent oral pathology at early stages. The leading paediatric dentistry academies agree that the first time the child visits the dental office should coincide with the eruption of the first milk tooth and no later than the first birthday, meaning when the child is still a baby.
This early first visit has numerous positive aspects, as it facilitates the establishment of a “dental home”, which is comparable in dentistry to the establishment of the “medical home” with the paediatrician from birth. The need to create this link means that, with increasing frequency, paediatric dentists visit babies, thus desensitizing the child population in the dental environment and making the first contact with the dentist simple, brief and positive to establish preventive measures.
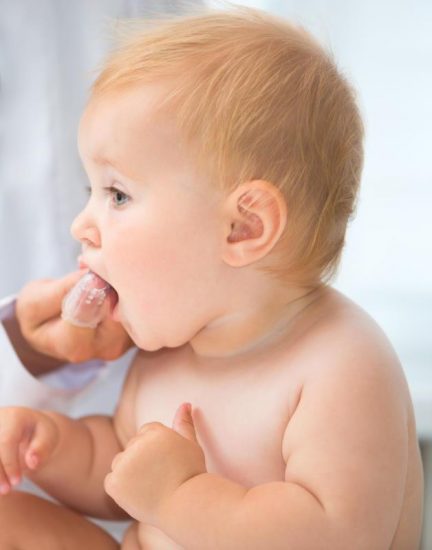

Oral Hygiene in babies
The baby’s teeth should be cleaned from their eruption with a bristle brush (not silicone bristles or gauze). In addition, it is essential to use a toothpaste with 1000 parts per million (ppm) of fluoride in the amount of “grain of rice”, at least twice a day.
From the eruption of the temporary teeth, if these have a very close contact, it is suggested passing the floss between the contact areas every night to prevent interproximal (in between teeth) caries lesions.
Should caries be treated in babies?
The answer is yes, without a doubt. We know that carious lesions in primary teeth develop more quickly and frequently affect the nerve tissue (pulpal tissue) of the tooth. This occurs due to the special characteristics of primary teeth.
The absence or postponement of treatment of a decayed tooth can lead to pain, infection and inflammation. In addition, it should be taken into account that sometimes the tooth with an extensive carious lesion and great destruction cannot be treated and its extraction is required. In the latter case, chewing, esthetics, facial, bone and muscle development will be affected, as well as the maintenance of space in the event that we are talking about the loss of a temporary tooth.